STORMWATER QUALITY ASSESSMENT AND BMP PRIORITIZATION FACT SHEET
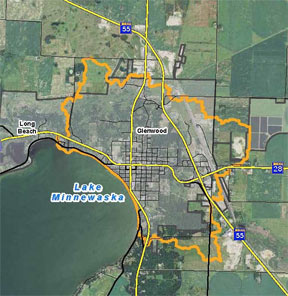 The Pope Soil and Water Conservation District hired Houston Engineering in 2015 to provide professional services to complete an assessment and analysis of approximately 1,796 acres including the storm water conveyance system affecting water quality and contributing runoff to Lake Minnewaska. The project would result in quantifying water quality of runoff reaching the lake, the rate, and the volume. The storm sewer system would be assessed using P8 a water quality computer model to identify, prioritize the sources of TSS, TN, and TP reaching Lake Minnewaska.
The Pope Soil and Water Conservation District hired Houston Engineering in 2015 to provide professional services to complete an assessment and analysis of approximately 1,796 acres including the storm water conveyance system affecting water quality and contributing runoff to Lake Minnewaska. The project would result in quantifying water quality of runoff reaching the lake, the rate, and the volume. The storm sewer system would be assessed using P8 a water quality computer model to identify, prioritize the sources of TSS, TN, and TP reaching Lake Minnewaska.
The project is intended to provide an effective means for the District to complete this assessment and analysis of this sub watershed area contributing runoff to Lake Minnewaska and create a suite of BMP solutions that will be prioritized to target the highest sources of TSS, TN, and TP reductions and include a cost benefit analysis per source (TSS, TN, and TP). The information included in this project will be the GIS shapefiles that will include annual yields of TSS, TN, and TP by project.
RAVINE REPAIR PROJECT FACT SHEET
The City of Glenwood (City), Pope Soil and Water Conservation District (SWCD) and Widseth Smith & Nolting (WSN) have taken an active roll in protecting the water quality to Lake Minnewaska this was accomplished through partnership and identifying project areas in the Stormwater Management Plan. The City was divided into 5 drainage areas. State Highways contribute runoff through the City. Estimated runoff in the Dairyland Basin ranges from 39 to 97 minutes before the stormwater reaches Lake Minnewaska. Stream monitoring has shown that most of the pollutant loading is coming in storm events.
The highest priority projects were located in the Dairyland Basin. This covers 462 acres with only 26% of that within the City and has 82.9 acres of impervious surfaces and 379.1 acres of pervious surface. Ravines were found originating from highway 55 and have been the worst in the last 10 years. The ravines measure 20′ to 30′ deep in some places. The project repaired the ravine using 3 check dams, an inlet structure, underground water lines, a control structure, and rock rip rap.